ASP 460 2.0 Data Visualization
Dr Thiyanga Talagala
Principal Component Analysis
1 / 26
PCA
Finding low-dimensional combinations (or projections) of high dimensional data that capture most of the variability in the original data.
Objective: Take P variables X1,X2,X3,...Xp and find combinations of these to produce variables (components) Z1,Z2...Zp that are uncorrelated.
Number of PCs = Number of variables in the original data.
- The components are ordered so that Z1 captures the largest proportion of the data, Z2 captures the next largest proportion of the variability
Var(Z1)≥Var(Z2)...≥Var(Zp)
2 / 26
PCA (cont.)
If original variables are uncorrelated then PCA does nothing at all. The PCs are the same as the original data.
PCs are formed by calculating the eigen vectors and eigen values of the data covariance matrix.
3 / 26
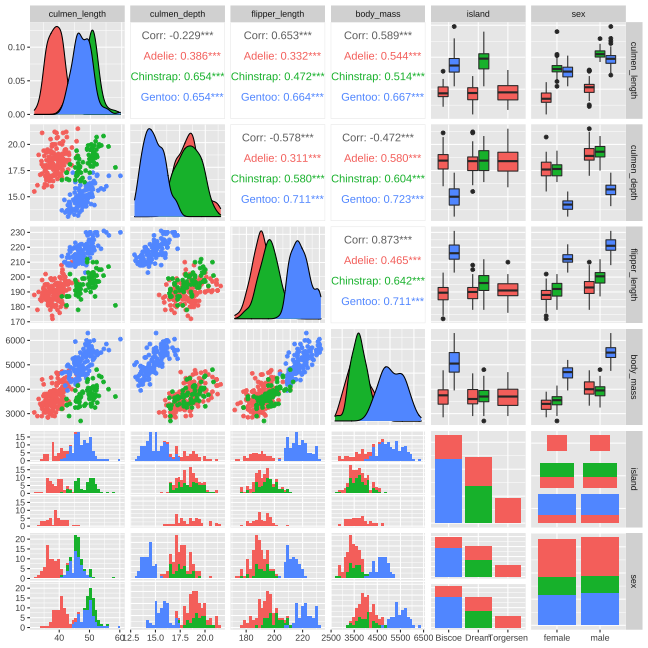
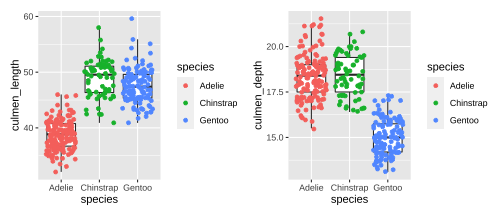
Data
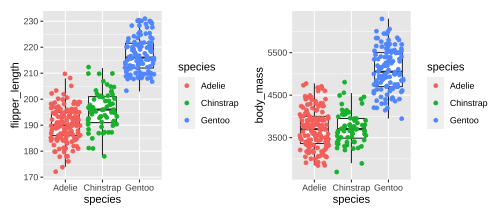
Rows: 344Columns: 8$ species <fct> Adelie, Adelie, Adelie, Adelie, Adelie, Adelie, Adel…$ island <fct> Torgersen, Torgersen, Torgersen, Torgersen, Torgerse…$ bill_length_mm <dbl> 39.1, 39.5, 40.3, NA, 36.7, 39.3, 38.9, 39.2, 34.1, …$ bill_depth_mm <dbl> 18.7, 17.4, 18.0, NA, 19.3, 20.6, 17.8, 19.6, 18.1, …$ flipper_length_mm <int> 181, 186, 195, NA, 193, 190, 181, 195, 193, 190, 186…$ body_mass_g <int> 3750, 3800, 3250, NA, 3450, 3650, 3625, 4675, 3475, …$ sex <fct> male, female, female, NA, female, male, female, male…$ year <int> 2007, 2007, 2007, 2007, 2007, 2007, 2007, 2007, 2007… species island bill_length_mm bill_depth_mm Adelie :152 Biscoe :168 Min. :32.10 Min. :13.10 Chinstrap: 68 Dream :124 1st Qu.:39.23 1st Qu.:15.60 Gentoo :124 Torgersen: 52 Median :44.45 Median :17.30 Mean :43.92 Mean :17.15 3rd Qu.:48.50 3rd Qu.:18.70 Max. :59.60 Max. :21.50 NA's :2 NA's :2 flipper_length_mm body_mass_g sex year Min. :172.0 Min. :2700 female:165 Min. :2007 1st Qu.:190.0 1st Qu.:3550 male :168 1st Qu.:2007 Median :197.0 Median :4050 NA's : 11 Median :2008 Mean :200.9 Mean :4202 Mean :2008 3rd Qu.:213.0 3rd Qu.:4750 3rd Qu.:2009 Max. :231.0 Max. :6300 Max. :2009 NA's :2 NA's :24 / 26
Data Cleaning
# A tibble: 6 × 8 species island culmen_length culmen_depth flipper_length body_mass sex year <fct> <fct> <dbl> <dbl> <int> <int> <fct> <int>1 Adelie Torge… 39.1 18.7 181 3750 male 20072 Adelie Torge… 39.5 17.4 186 3800 fema… 20073 Adelie Torge… 40.3 18 195 3250 fema… 20074 Adelie Torge… 36.7 19.3 193 3450 fema… 20075 Adelie Torge… 39.3 20.6 190 3650 male 20076 Adelie Torge… 38.9 17.8 181 3625 fema… 2007 species island culmen_length culmen_depth flipper_length Adelie :146 Biscoe :163 Min. :32.10 Min. :13.10 Min. :172 Chinstrap: 68 Dream :123 1st Qu.:39.50 1st Qu.:15.60 1st Qu.:190 Gentoo :119 Torgersen: 47 Median :44.50 Median :17.30 Median :197 Mean :43.99 Mean :17.16 Mean :201 3rd Qu.:48.60 3rd Qu.:18.70 3rd Qu.:213 Max. :59.60 Max. :21.50 Max. :231 body_mass sex year Min. :2700 female:165 Min. :2007 1st Qu.:3550 male :168 1st Qu.:2007 Median :4050 Median :2008 Mean :4207 Mean :2008 3rd Qu.:4775 3rd Qu.:2009 Max. :6300 Max. :20095 / 26
6 / 26
Artwork by @allison_horst
7 / 26
Artwork by @allison_horst
8 / 26
PCA
Select numerical variables
scale the data to 0 mean and unit variance.
Perform PCA.
9 / 26
PCA
Standard deviations (1, .., p=4):[1] 1.6569115 0.8821095 0.6071594 0.3284579Rotation (n x k) = (4 x 4): PC1 PC2 PC3 PC4culmen_length 0.4537532 -0.60019490 -0.6424951 0.1451695culmen_depth -0.3990472 -0.79616951 0.4258004 -0.1599044flipper_length 0.5768250 -0.00578817 0.2360952 -0.7819837body_mass 0.5496747 -0.07646366 0.5917374 0.5846861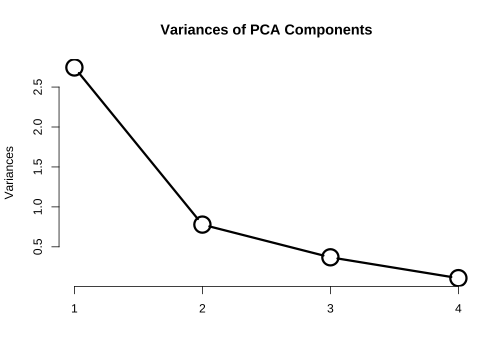
10 / 26
Standard deviations associated with PCs
summary(pca)Importance of components: PC1 PC2 PC3 PC4Standard deviation 1.6569 0.8821 0.60716 0.32846Proportion of Variance 0.6863 0.1945 0.09216 0.02697Cumulative Proportion 0.6863 0.8809 0.97303 1.00000PCA rotation matrix
pca$rotation PC1 PC2 PC3 PC4culmen_length 0.4537532 -0.60019490 -0.6424951 0.1451695culmen_depth -0.3990472 -0.79616951 0.4258004 -0.1599044flipper_length 0.5768250 -0.00578817 0.2360952 -0.7819837body_mass 0.5496747 -0.07646366 0.5917374 0.584686111 / 26
Predict PCs
predict(pca, newdata=tail(penguins)) PC1 PC2 PC3 PC4[1,] -0.4507833 -0.06535056 -0.7461058 -0.01287014[2,] 0.5526429 -2.34408404 -0.8679388 -0.38749681[3,] -0.7388017 -0.24778208 -0.3155918 -0.73267497[4,] -0.3673370 -0.98959040 -0.8866618 0.19556826[5,] 0.4916198 -1.48261810 -0.3294640 -0.55003132[6,] -0.2130962 -1.25965815 -0.7648157 -0.10807071tail(pca$x) PC1 PC2 PC3 PC4328 -0.4507833 -0.06535056 -0.7461058 -0.01287014329 0.5526429 -2.34408404 -0.8679388 -0.38749681330 -0.7388017 -0.24778208 -0.3155918 -0.73267497331 -0.3673370 -0.98959040 -0.8866618 0.19556826332 0.4916198 -1.48261810 -0.3294640 -0.55003132333 -0.2130962 -1.25965815 -0.7648157 -0.1080707112 / 26
PCA
PC1 PC2 PC3 PC41 -1.850808 -0.03202119 0.23454869 0.52760262 -1.314276 0.44286031 0.02742880 0.40112303 -1.374537 0.16098821 -0.18940423 -0.52786754 -1.882455 0.01233268 0.62792772 -0.47218265 -1.917096 -0.81636958 0.69999797 -0.19612136 -1.770356 0.36567266 -0.02841769 0.5046092Original data
# A tibble: 6 × 8 species island culmen_length culmen_depth flipper_length body_mass sex year <fct> <fct> <dbl> <dbl> <int> <int> <fct> <int>1 Adelie Torge… 39.1 18.7 181 3750 male 20072 Adelie Torge… 39.5 17.4 186 3800 fema… 20073 Adelie Torge… 40.3 18 195 3250 fema… 20074 Adelie Torge… 36.7 19.3 193 3450 fema… 20075 Adelie Torge… 39.3 20.6 190 3650 male 20076 Adelie Torge… 38.9 17.8 181 3625 fema… 200713 / 26
Combine PCA + original data
pcadf <- data.frame(pca$x)penguins_pca <- bind_cols(penguins, pcadf)head(penguins_pca )# A tibble: 6 × 12 species island culmen_length culmen_depth flipper_length body_mass sex year <fct> <fct> <dbl> <dbl> <int> <int> <fct> <int>1 Adelie Torge… 39.1 18.7 181 3750 male 20072 Adelie Torge… 39.5 17.4 186 3800 fema… 20073 Adelie Torge… 40.3 18 195 3250 fema… 20074 Adelie Torge… 36.7 19.3 193 3450 fema… 20075 Adelie Torge… 39.3 20.6 190 3650 male 20076 Adelie Torge… 38.9 17.8 181 3625 fema… 2007# … with 4 more variables: PC1 <dbl>, PC2 <dbl>, PC3 <dbl>, PC4 <dbl>14 / 26
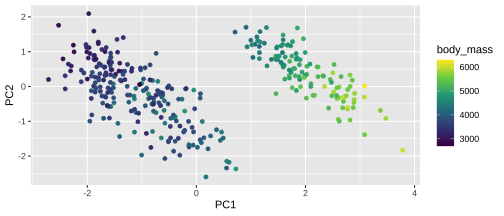
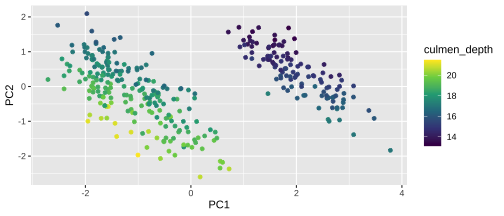
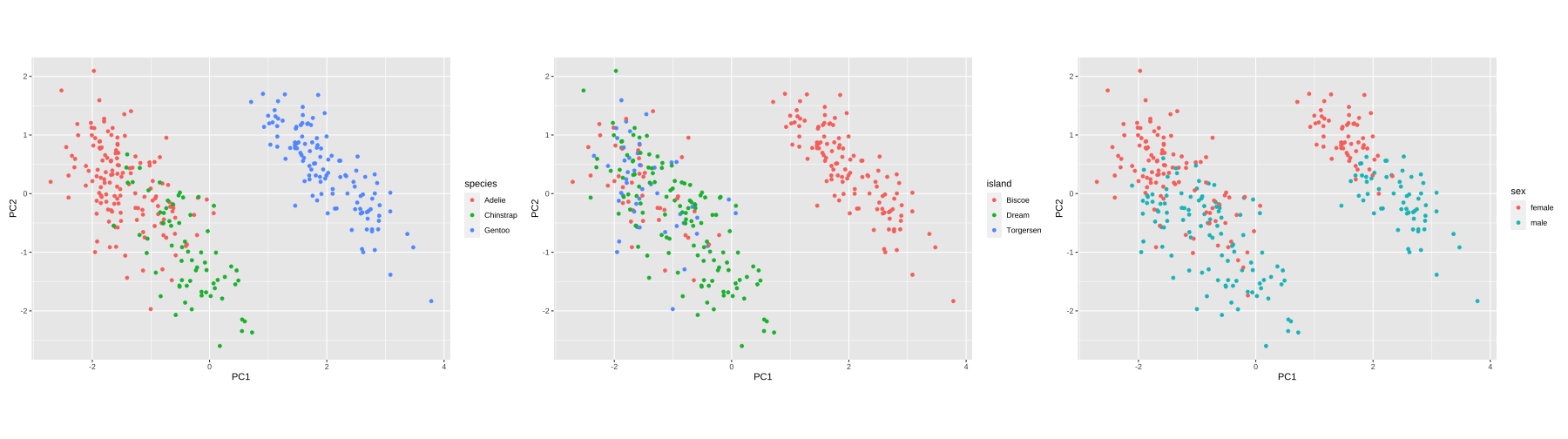
PC1 vs PC2
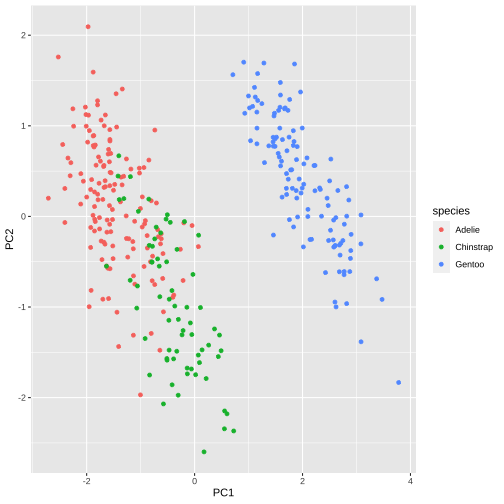
15 / 26
Plotting PCA
Standard deviations (1, .., p=4):[1] 1.6569115 0.8821095 0.6071594 0.3284579Rotation (n x k) = (4 x 4): PC1 PC2 PC3 PC4culmen_length 0.4537532 -0.60019490 -0.6424951 0.1451695culmen_depth -0.3990472 -0.79616951 0.4258004 -0.1599044flipper_length 0.5768250 -0.00578817 0.2360952 -0.7819837body_mass 0.5496747 -0.07646366 0.5917374 0.5846861[1] 68.633893 19.452929 9.216063 2.697115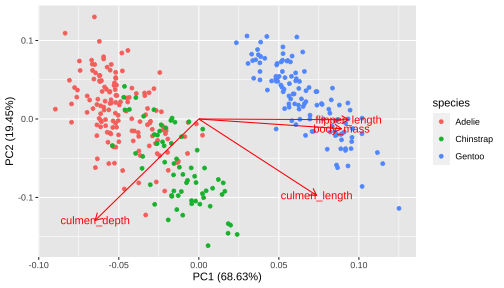
16 / 26
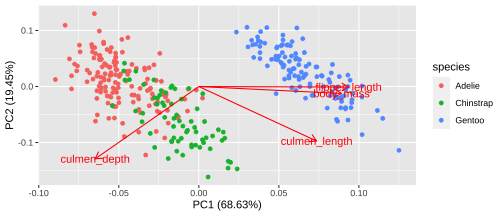
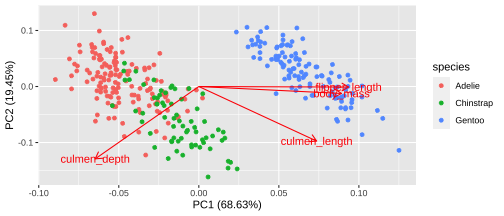
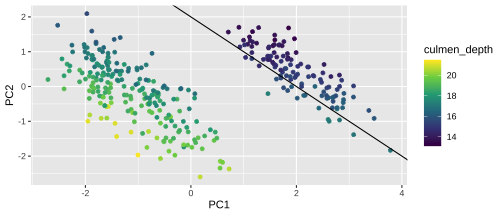
Biplot - plot each variables coefficients inside a unit circle
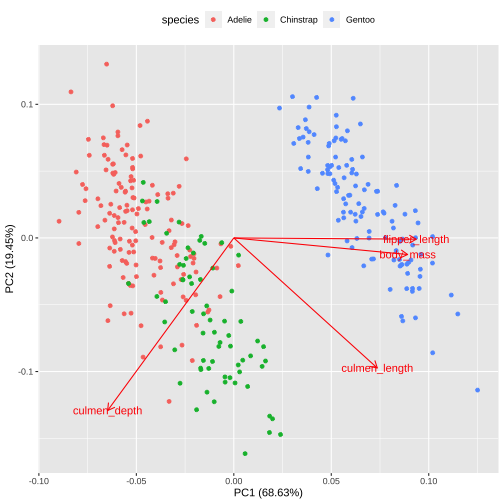
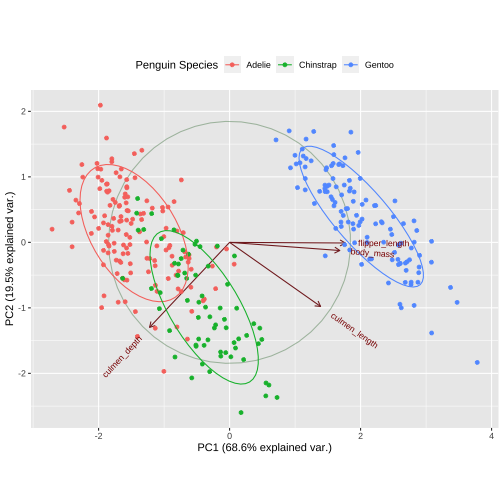
PCA rotation
PC1 PC2 PC3 PC4culmen_length 0.4537532 -0.60019490 -0.6424951 0.1451695culmen_depth -0.3990472 -0.79616951 0.4258004 -0.1599044flipper_length 0.5768250 -0.00578817 0.2360952 -0.7819837body_mass 0.5496747 -0.07646366 0.5917374 0.584686117 / 26
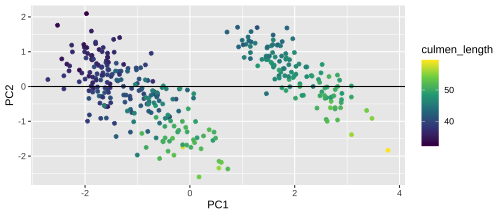
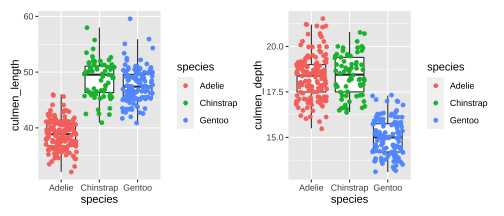
Plotting PCA - PC1
18 / 26
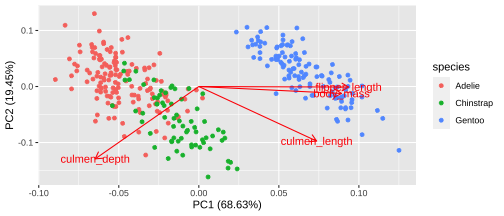
19 / 26
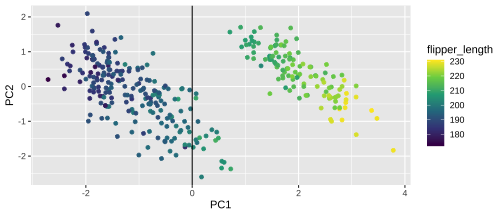
Plotting PCA - PC1
20 / 26
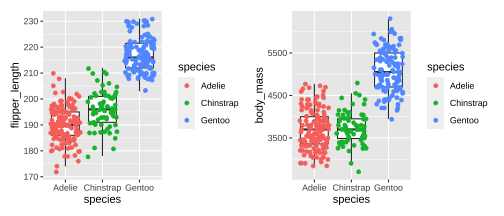
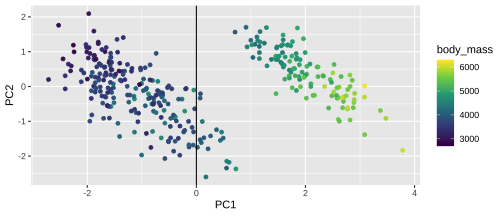
21 / 26
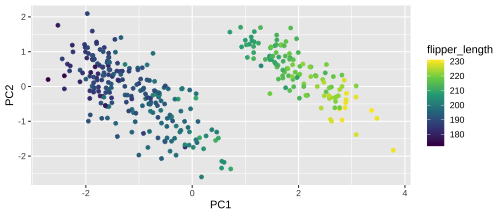
Plotting PCA - PC2
22 / 26
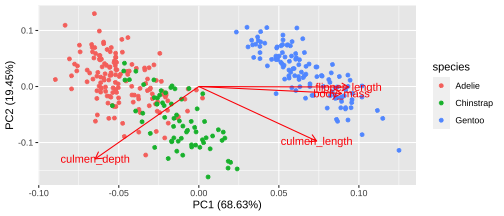
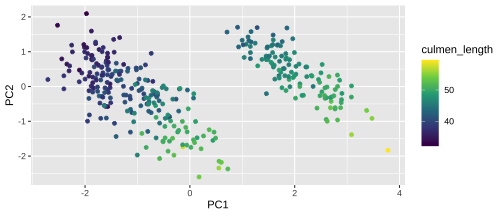
23 / 26
Plotting PCA - PC2
24 / 26
25 / 26
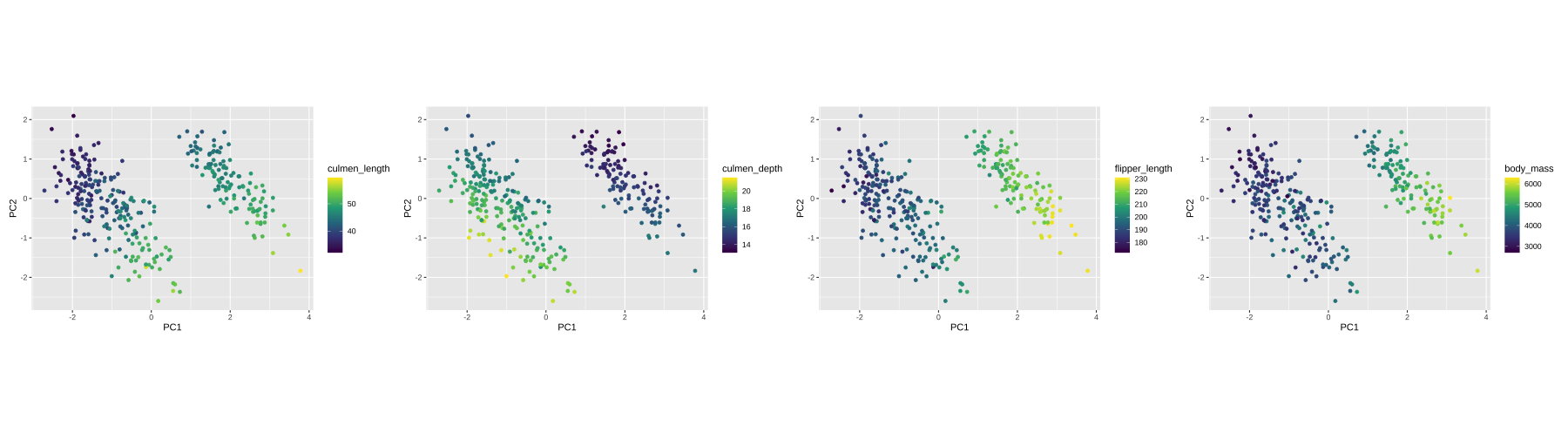
Visualising instance space
26 / 26