ASP 460 2.0 Data Visualization
Dr Thiyanga Talagala
4. Best Graphical Practice
Cognitive Principles
Less conginitive effort to read the chart (what is presented) and save the time to think about the content of the chart
- Good visualizations take advantage of the human visual system's ability to process information with little effort.
Cognitive Principles
Less conginitive effort to read the chart (what is presented) and save the time to think about the content of the chart
- Good visualizations take advantage of the human visual system's ability to process information with little effort.
Preattentive graph perception
It requires no conscious effort from the viewer to do understand what is presented through the design. It's automated and takes between 200-500 milliseconds to complete in the spatial memory.
Cognitive Principles
Less conginitive effort to read the chart (what is presented) and save the time to think about the content of the chart
- Good visualizations take advantage of the human visual system's ability to process information with little effort.
Preattentive graph perception
It requires no conscious effort from the viewer to do understand what is presented through the design. It's automated and takes between 200-500 milliseconds to complete in the spatial memory.
(Spatial working memory entails the ability to keep spatial information active in working memory over a short period of time.)
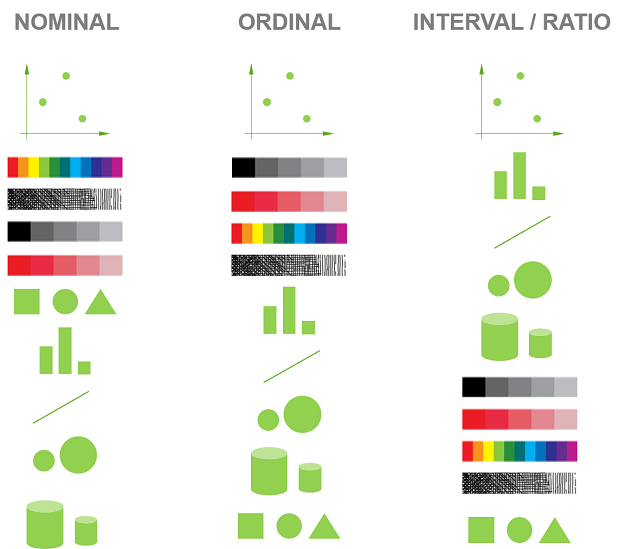
Preattentive visual properties
Color
Form: collinearity, curvature, marks, shape, size, spatial grouping, length, width, breadth
Spatial position: 2D, 3D
Movement: flicker, movement
These are processed in our sensory memory without our conscious thoughts (without having knowledge of something).
Inclass discussion
Cognitive principles
1. Proximity
2. Similarity
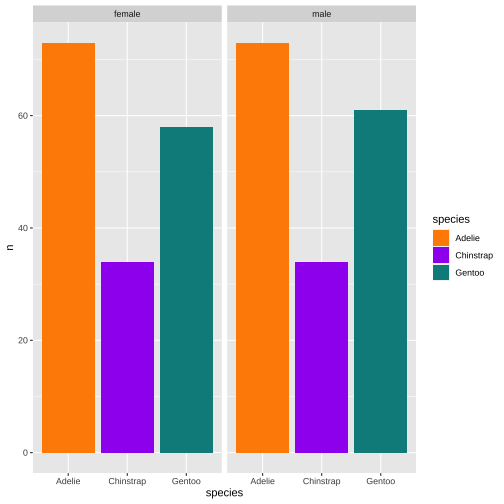
3. Common region
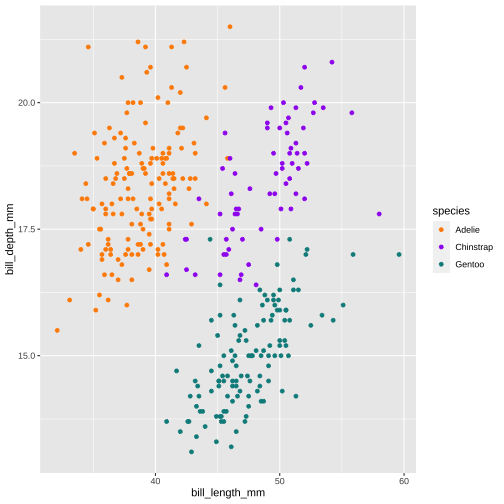
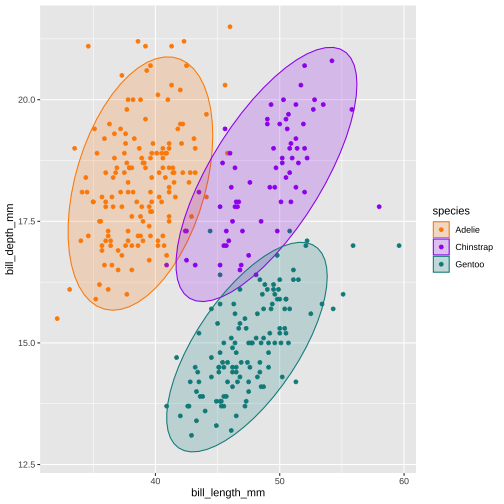
4. Common fate
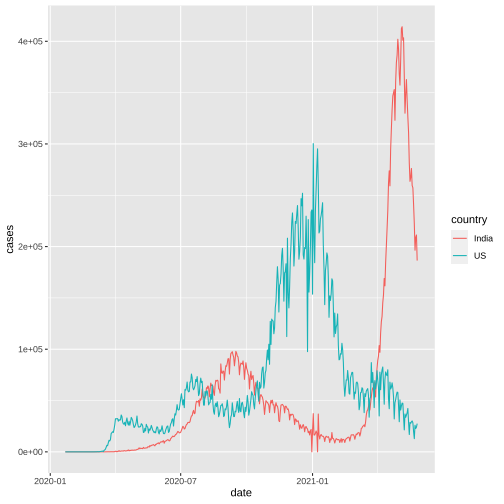
4. Common fate

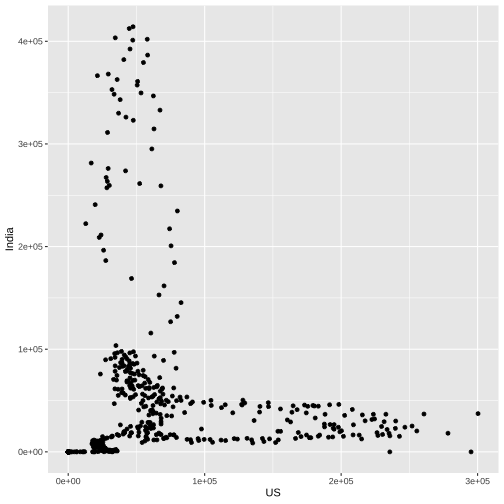
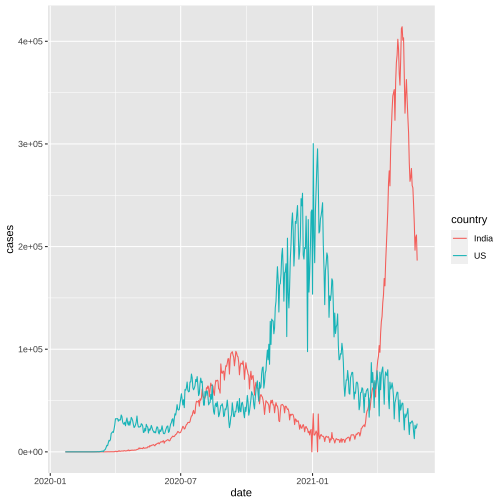
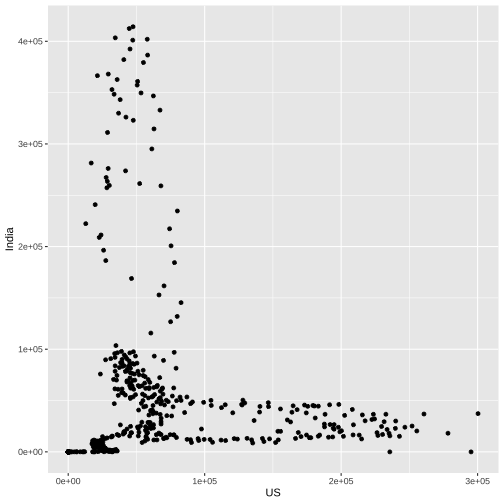
US vs India
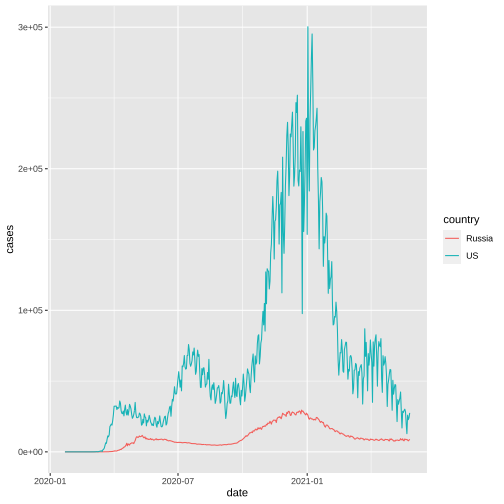
US vs Russia
US vs India
US vs Russia
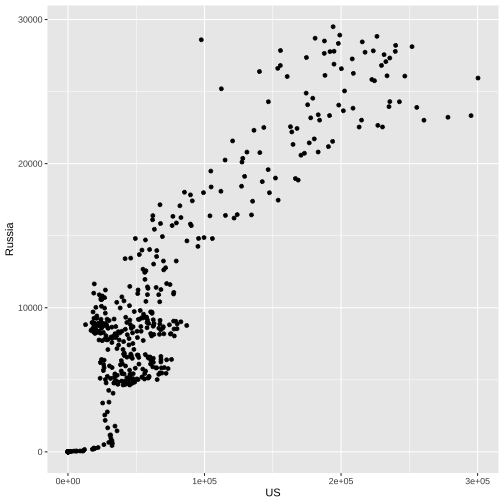
5. Working memory
More than seven categories decrease readability and increase comprehension time.
7. Easy comparisons
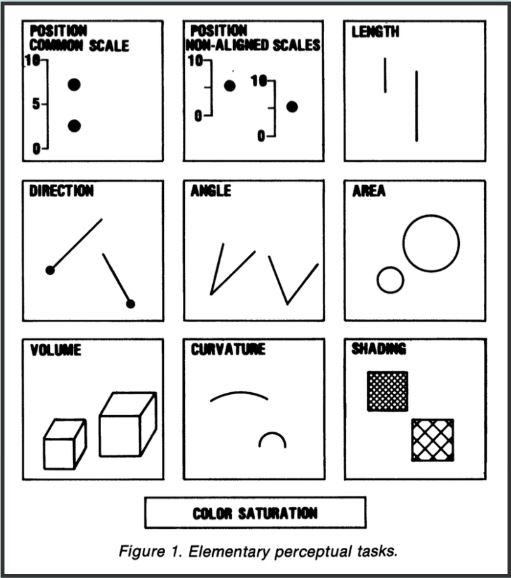
Position (common scale)
Position (nonaligned scale)
Length, direction, angle, slope
Area
Volume, density, curve
Shading, color saturation, colour hue
Discriminable shape
Indiscriminable shape
7. Easy comparisons: Example
colour, discriminable shape, indiscriminable shape
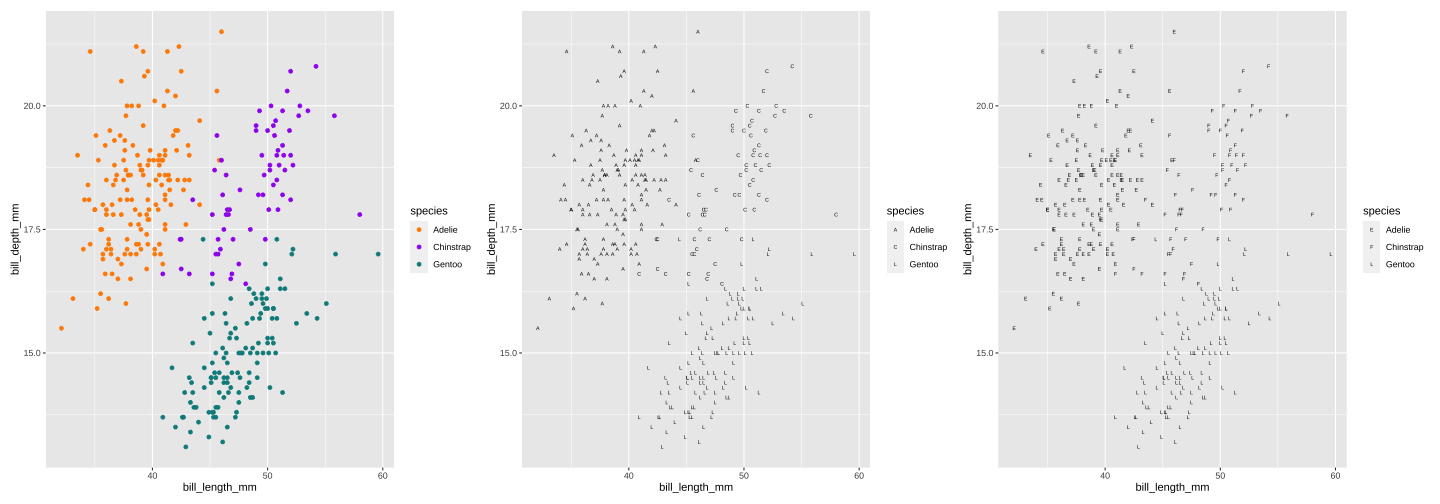
7. Easy comparisons: Example
In 1980s, statisticians William Cleveland and Robert McGill ran some experiments with human volunteers, measuring how accurately they were able to perceive the quantitative information encoded by different cues.
Jock D. Mackinlay
Jock D. Mackinlay received his PhD in computer science from Stanford University, where he pioneered the automatic design of graphical presentations of relational information.
Which visual encoding method is best for you?